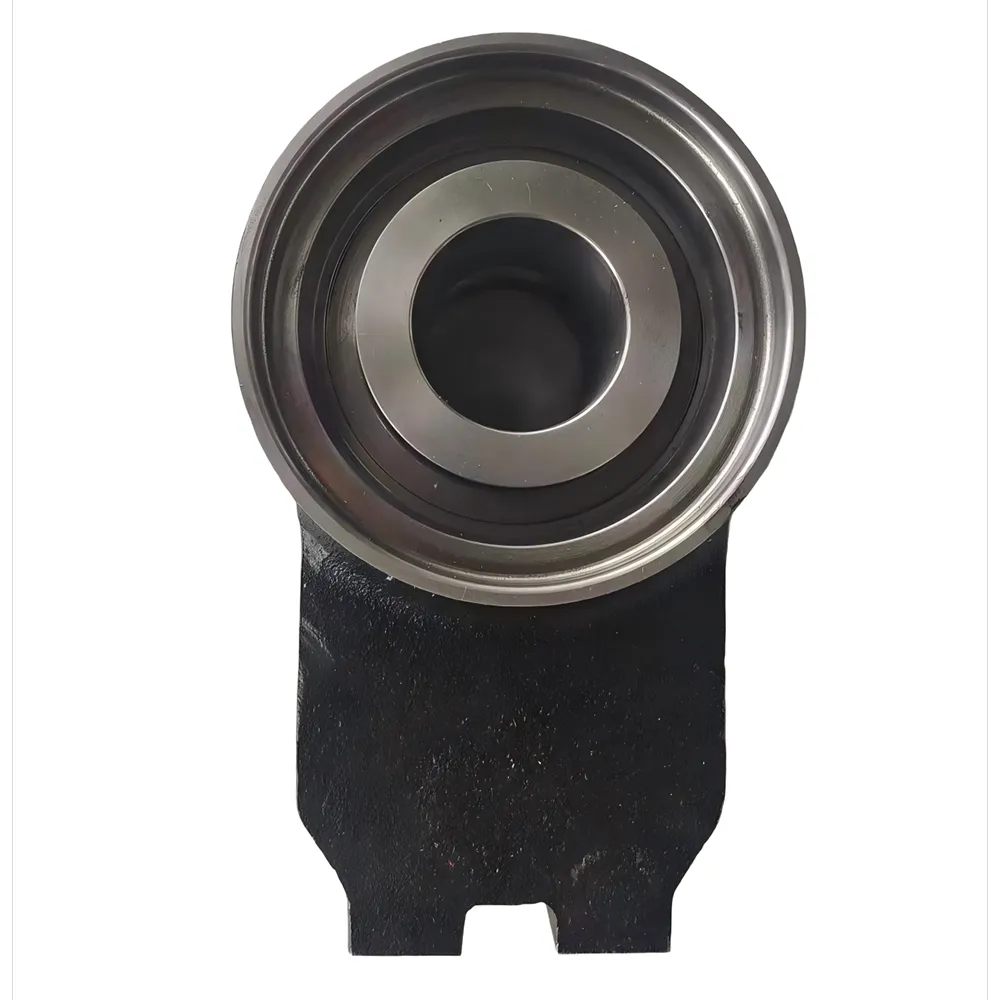
The chassis support system refers to the integrated network of structural components that:
Distribute operational loads across the machine's frame
Provide mounting points for critical systems
Absorb vibration and shock loads
Maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions
✔ Load Distribution - Spreads weight evenly across the undercarriage
✔ Structural Reinforcement - Strengthens high-stress areas of the frame
✔ Component Protection - Shields vital systems from impact damage
✔ Vibration Damping - Reduces harmonic stresses on the machine
✔ Operational Stability - Maintains balance during dynamic operations
1. Main Frame Rails
Primary longitudinal structural members
Typically box-section or C-channel design
2. Cross Members
Transverse structural connectors
Provide torsional rigidity
3. Reinforcement Plates
Added at high-stress points
Prevent cracking and metal fatigue
4. Mounting Brackets
For engine, transmission, and implement attachments
Designed for specific load paths
5. Impact Protection
Skid plates and wear surfaces
Abrasion-resistant materials
Materials and Manufacturing
✔ High-Strength Steel Alloys - ASTM A514, T1, or equivalent
✔ Precision Laser Cutting - For accurate component fabrication
✔ Robotic Welding - Consistent, high-penetration welds
✔ Stress-Relief Treatment - Post-weld heat treatment
✔ Advanced Coatings - Industrial-grade corrosion protection
1. Fatigue-Resistant Engineering
Finite element analysis (FEA) optimized
Eliminates stress concentrations
2. Modular Construction
Allows section replacement
Reduces downtime for repairs
3. Serviceability Considerations
Easy access to lubrication points
Simplified inspection pathways
4. Weight Optimization
Strength-to-weight ratio maximization
Without compromising durability
5. Impact Absorption
Energy-dissipating designs
Shock-absorbing mount systems
Extended Equipment Life - Reduces frame fatigue and cracking
Improved Stability - Enhances operational safety
Reduced Maintenance - Minimizes structural repairs
Better Performance - Maintains proper component alignment
Higher Resale Value - Preserves structural integrity
1. Earthmoving Equipment
Excavators
Bulldozers
Motor graders
2. Material Handling
Wheel loaders
Backhoe loaders
Skid steers
3. Heavy Haulage
Dump trucks
Articulated haulers
Mining trucks
4. Specialized Machinery
Cranes
Piling rigs
Tunnel boring machines
5. Road Construction
Asphalt pavers
Compactors
Milling machines
Best Practices for Longevity:
Proper Torque Procedures - For all structural fasteners
Regular Alignment Checks - Prevent uneven stress distribution
Controlled Welding Repairs - Follow OEM specifications exactly
Corrosion Prevention - Regular cleaning and coating maintenance
Critical Inspection Points:
Monthly: Visual inspection for cracks or deformation
Quarterly: Fastener integrity verification
Annually: Non-destructive testing (NDT) for hidden defects
After Major Impacts: Full structural assessment
Common Failure Modes
Fatigue Cracking - From cyclic loading
Corrosion Damage - Particularly in coastal environments
Impact Deformation - From collisions or overloads
Weld Failures - Poor quality or improper repairs
Bolt Loosening - Vibration-induced fastener fatigue
When specifying chassis supports:
Machine Specifications - Exact make/model compatibility
Duty Cycle - Match to expected operational intensity
Environmental Factors - Corrosion resistance requirements
OEM vs. Aftermarket - Balance cost vs. guaranteed fitment
Upgrade Potential - For modified or high-performance applications
Quality components meet:
✔ ISO 9001 Quality Management
✔ CE Certification for EU markets
✔ OSHA Safety Requirements
✔ OEM Engineering Specifications
✔ ASTM Material Standards
A well-designed chassis support system:
✔ Withstands years of brutal service
✔ Protects expensive components
✔ Ensures operator safety
✔ Maintains machine productivity
Investing in quality chassis support pays dividends through extended equipment life and reduced operating costs.